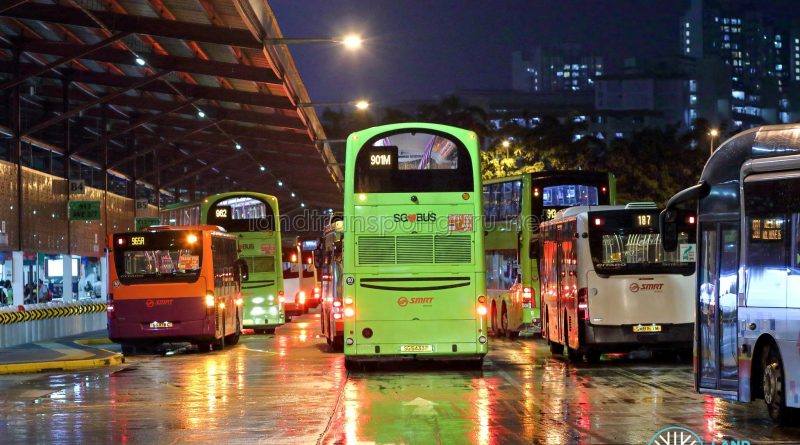
Bus Interchanges and Bus Terminals are public transport facilities that are used as terminating points for bus routes.
In Singapore, bus interchanges and terminals are key transport nodes that support the commuting needs of their localities. Under the hub-and-spoke public transport model, buses are frequently used for last-mile connections, and these transport facilities are thus also constructed near MRT stations. Modern bus interchanges are built as air-conditioned mixed-use developments, called Integrated Transport Hubs (ITHs).
As of 2024, there are 30 bus interchanges in operation, and about 17 bus terminals served by public bus services.
Locality Map
Brief Overview
Bus terminals in Singapore were originally built and managed by individual bus operators. After the 1973 consolidation that formed Singapore Bus Service (SBS), the company initiated a terminal improvement program to enhance facilities. This included adding more parking spaces, crew offices and rest areas, sheltered commuter waiting areas, toilets, and food stalls.
The development of bus terminals has been closely aligned with Singapore’s town planning. Since the late 1970s, densely-populated New Towns have been designed with a centrally-located bus interchange. Feeder services connected residents within these towns to their respective bus interchanges.
In 1983, the Government assumed responsibility for building and developing bus interchanges and terminals. The opening of the MRT system in the late 1980s led to the placement of bus interchanges near MRT stations to facilitate the integration of bus and train services. Since 2002, the government has been upgrading neighbourhood bus interchanges into Integrated Transport Hubs (ITHs), which are air-conditioned, mixed-use developments.
A more detailed write-up of Singapore’s bus interchanges and terminals can be found below.
List of Bus Interchanges
Bus Interchanges are large commuter facilities serving multiple bus routes, with most also offering connections to the Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) network. They are integral to Singapore’s hub-and-spoke public transportation network, where commuters frequently rely on buses for last-mile connections.
All bus interchanges currently in operation are listed here:
| Bus Interchange | Bus Services |
| Ang Mo Kio | 22, 24, 25, 73, 86, 130, 133, 135, 136, 138, 166, 169, 261, 262, 265, 269 |
| Bedok | 7, 9, 14, 16/16M, 17, 26, 30, 30e, 32, 33, 35/35M, 38, 40, 60, 69, 87, 155, 168, 196, 197, 222, 225G/225W, 228, 229, 401, 854, 854e |
| Bishan | 50, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 410G/410W |
| Boon Lay | 30, 79, 154, 157, 172, 174, 174e, 178, 179, 180, 181/181M, 187, 192, 193, 194, 198, 199, 240, 241, 242, 243G/243W, 246, 249, 251, 252, 405 |
| Buangkok |
110, 114, 156 |
| Bukit Batok | 61, 77, 106, 173, 177, 189, 852, 941, 945, 947, 990, 991, 992 |
| Bukit Merah | 5, 16/16M, 57, 75, 123, 131, 132, 139, 153, 167, 176, 198, 272, 273, 851 |
| Bukit Panjang | 176, 180, 920, 922, 970, 972/972M, 973, 975, 976, 979 |
| Choa Chu Kang | 67, 172, 188, 188e, 190, 300, 301, 302, 307, 925, 927, 976, 983, 985, 991 |
| Clementi | 7, 14, 96, 99, 147, 156, 165, 166, 173, 175, 196, 282, 284, 285 |
| Eunos | 22, 60, 61, 63/63M, 76, 93, 94, 150, 154 |
| HarbourFront | 65, 80, 93, 123M, 124, 188, 188e, 855, 963, 963e |
| Hougang Central | 27, 51, 74, 89, 89e, 102, 107/107M, 112, 113, 116, 132, 147, 151, 153, 161, 165, 324, 325, 329 |
| Joo Koon | 99, 182/182M, 253, 254, 255, 257, 258, 974 |
| Jurong East | 41, 49, 51, 52, 66, 97, 97e, 98/98M, 105, 143/143M, 183, 197, 333, 334, 335, 506, 993 |
| Jurong Town Hall | 78, 79, 160, 870, CW3, CW4, CW4S |
| Pasir Ris | 3, 5, 6, 12, 12e, 15, 17, 21, 46, 58, 68, 88, 354, 358, 359, 403, 518, 518A |
| Punggol | 3, 34, 43/43M, 43e, 50, 62, 82, 83, 84G/84W, 85, 117/117M, 118, 119, 136, 381, 382G/382W, 384, 386 |
| Sembawang | 117/117M, |
| Sengkang | 80, 83, 86, 87, 159, 163, 371, 372, 374, 965 |
| Serangoon | 100, 101, 103, 105, 109, 158, 315, 317, 506 |
| Tampines | 3, 4, 8, 10, 19, 20, 23, 28, 29, 31, 37, 38, 65, 67, 68, 69, 72, 81, 127, 291, 292, 293, 296, 969 |
| Tampines Concourse | 39 |
| Tampines North |
18, 129, 298/298X |
| Tengah |
870, 871, 992 |
| Toa Payoh | 8, 26, 28, 31, 73, 88, 90, 139, 141, 142, 143, 145, 155, 157, 159, 163, 230, 231, 232, 235, 238 |
| Woodlands (Temporary Bus Interchange) |
925/925M, 950, 961/961M, 965 |
| Woodlands (Integrated Transport Hub) |
161, 168, 169, 178, 187, 856, 858, 900, 901/901M, 902, 903/903M, 904, 911, 912/912M, 913/913M, 960, 960e, 962, 963, 963e, 964, 966, 969 |
| Yio Chu Kang | 13, 70/70M, 71, 72, 76, 162, 825, 860 |
| Yishun | 39, 85, 103, 171, 800, 801, 803, 804, 805, 806, 807, 811, 812, 851, 851e, 852, 853/853M, 854, 854e, 855, 856, 857, 859, 860, AC7 |
Integrated Transport Hub (ITH)
Several bus interchanges are designated as Integrated Transport Hubs or ITHs. These interchanges are located near MRT stations and have fully air-conditioned passenger concourses. These are often built within commercial and residential buildings as part of an integrated development.
There are currently 12 ITHs in Singapore, which are, in order of opening date:
- Toa Payoh (May 2002)
- Sengkang (Jan 2003)
- Ang Mo Kio (Apr 2007)
- Boon Lay (Dec 2009)
- Serangoon (Sep 2011)
- Clementi (Nov 2011)
- Bedok (Nov 2014)
- Joo Koon (Nov 2015)
- Bukit Panjang (Sep 2017)
- Yishun (Sep 2019)
- Woodlands (Jun 2021)
- Buangkok (Dec 2024)
List of Bus Terminals
Bus Terminals are smaller facilities used as regional terminating points for bus services. Compared to bus interchanges, they handle fewer bus services and often have more basic commuter facilities. Some bus terminals do not allow for passenger boarding and alighting.
All bus terminals currently in operation are listed here:
| Bus Terminal | Bus Services |
| Beach Station | 123, Sentosa Bus A, Sentosa Bus B |
| Buona Vista | 32, 48, 74, 91, 145, 185, 191, 200 |
| Changi Airport Terminal 2 | 24, 27, 34, 36, 53, 110, 858 |
| Changi Business Park | 47, 118 |
| Changi Village | 2, 29, 59, 109 |
| Gali Batu | 75, 184 |
| Ghim Moh | 92, 100, 111 |
| JB Sentral | 160, 170X, 950, other JB local bus routes |
| Kampong Bahru | 2, 12, 12e, 54, 120, 122, 174, 174e, 190 |
| Kent Ridge | 10, 33, 95, 151, 200, 201, NUS A1, NUS A2 |
| Larkin | 170, other JB local bus routes |
| Lorong 1 Geylang | 11, 140, 141, 175, 853, 961/961M, 980, 985 |
| Marina Centre | 56, 77, 97, 97e, 195, 960, 960e |
| Queen Street | 170, CW2, SJE |
| Resorts World Sentosa | 123, RWS8, Sentosa Bus A |
| Saint Michael’s | 21, 124, 125, 129, 131, 186 |
| Shenton Way | 70, 106, 107, 121, 130, 133, 186, 400, 970 |
| Sims Place | 64, 134, 137 |
| Tuas | 192, 193, 247, 248, 248M |
| Upper East Coast | 13, 25, 43, 45, 46, 55, 137, 853M |
Ghim Moh and Sims Place are currently the only two roadside terminals left in Singapore. Another roadside terminus is located along Jalan Kembangan (outside Kembangan MRT), but this facility is not officially designated as a bus terminal.
JB Sentral and Larkin are located in Johor Bahru, Malaysia.
Bus Depots used as route termini
Some bus depots in Singapore are used as route termini of bus services, as follows:
| Bus Depot | Bus services |
| Ang Mo Kio | 45, 265, 268 |
| Bedok North | 18, 48 |
| Soon Lee | 185, 502/502A |
Private Bus Termini
These facilities are used only by private buses:
| Bus Terminal | Bus services |
| Little India | Little India Bus Services Private buses to/from workers’ dormitories |
| Prince George’s Park | NUS A1, NUS D2, NUS BTC, NUS K |
Bus Parks
Bus Park used to park buses only, with no boarding and alighting activities allowed:
| Bus Park | Remarks |
| Hougang Bus Park | Supports Hougang Central Int during construction of the Cross Island Line Hougang Station |
Upcoming Bus Interchanges & Terminals:
Works in Progress / Construction Tenders Issued
- Woodleigh Integrated Transport Hub
(Under Construction, projected opening in 2019 & delayed to end 2024) - Pasir Ris Integrated Transport Hub
(Under Construction, projected opening in 2025) - Punggol Coast Integrated Transport Hub
(Under Construction) - Jurong East Integrated Transport Hub (Jurong Gateway Hub)
(Under Construction; projected completion 2027) - Kallang Bus Interchange
(Integrated with Kallang Horizon BTO Project; Under Construction) - Beauty World Integrated Transport Hub
(Mixed-use Development at Bukit Timah; within Bukit V Mall) - Tuas Transport Hub
(Bus terminal at Tuas Port)
Under Planning
- Bedok South Integrated Transport Hub*
- Chencharu Bus Interchange
- Hougang Central Integrated Transport Hub*
- Tampines Integrated Transport Hub**
- Tampines North Integrated Transport Hub*
- Tengah Integrated Transport Hub*
- Tiong Bahru Integrated Transport Hub*
- Marina South Integrated Transport Hub^
- Woodlands North Integrated Transport Hub**
- Choa Chu Kang Integrated Transport Hub
* – As per URA Draft Master Plan 2019
^ – As per Land Transport Master Plan 2040
** – Mentioned as part of Draft Master Plan 2025
List of abolished Bus Interchanges and Terminals: In addition, several regular bus services terminate at bus stops which do not count as bus termini. These are: In the past, private bus companies built and operated their own bus termini. They were usually located along the roads and were plenty in number, adding to the difficulty of integrating various different bus routes. In the 1970s, smaller-scaled bus terminals were built, most of them by the Public Works Department (PWD) and the Housing and Development Board (HDB). The private bus companies would then rent these terminals for thousands of dollars per month. In the late 1970s, the construction of new towns resulted in the idea of regional bus interchanges to take over the roles of the bus terminals. This would improve efficiency and reduce overlapping of bus routes. Early bus interchanges were designed and built by the HDB, which was also the main architect of bus stops and other facilities for public transport. Starting in 1976, SBS started its Bus Terminal Improvement Programme, leading to the phase-out or relocation of 28 bus terminals. Many moved to major bus interchanges located at the centre of the new towns. In 1978, Jurong Bus Interchange was opened, being Singapore’s first bus interchange. With the construction of the MRT in the 1980s, bus transport in Singapore slowly adapted in favour of centralised bus interchanges that provide connections to the MRT, and the use of multiple feeder bus services to link up different parts of new towns with MRT stations. This was complemented by a 1981 Ministry of Communications report that evaluated the public bus system, and found that interchanges and terminals needed to be better coordinated with the development of new towns and MRT stations. In 1983, the Government and its statutory boards took over five bus interchanges and more than 50 roadside termini from SBS [Link], while also taking over the building and maintenance of all bus interchanges and termini in future. Bedok, Bukit Merah, Clementi, and Woodlands Interchanges were taken over by the HDB, while Jurong Interchange was taken over by the Jurong Town Corporation, and terminals were distributed among statutory boards in charge of the land they were built on. The cost of building the five bus interchanges, at roughly $9 million, was written off by SBS, as was the cost of the bus termini. Ownership would later be merged under the Land Transport Authority (LTA), which was formed in 1995. In 1996, Woodlands Regional Bus Interchange was opened. Built by the Mass Rapid Transit Corporation (MRTC), this novel design saw the bus interchange constructed underneath the elevated Woodlands MRT Station, to maximize space for the development of the surrounding town centre. Starting in the 2000s, bus interchange designs in residential towns evolved into Integrated Transport Hubs (ITHs), wherein bus interchanges are integrated into mixed-use developments. These air-conditioned facilities provide seamless links to MRT stations and adjoining commercial developments such as shopping malls. The first such interchange was Toa Payoh, which opened in May 2002. ITHs have since been integrated with shopping malls, condominiums, and even HDB flats, as was the case for Woodleigh. As of June 2021, there are eleven ITHs in Singapore, with more expected to be completed in the years to come. New bus interchanges have also been constructed to expand the capacity of existing bus interchanges. These are Tampines Concourse (opened 2016), Compassvale (opened 2017), and Jurong Town Hall (opened 2023). Bus termini have also been constructed on the roof slabs of train depots to maximize land use. These are Tuas (opened 2017) and Gali Batu (opened 2021). Today, construction of bus interchanges and terminals is commissioned by the Land Transport Authority (LTA). ITHs that are part of commercial buildings/condominiums/etc. are still built by private developers, but must follow LTA guidelines on architecture and commuter infrastructure. With the rollout of the Bus Contracting Model in 2016, all bus interchanges and terminals are bundled together with Bus Packages which are subsequently tendered out to bus operators. Therefore, each interchange or terminal has a designated anchor operator, which is almost always the bus operator with the largest operations at the facility. Anchor operators must operate and maintain the bus interchanges/terminals, along with all the equipment and systems provided within, and provide bus service information to passengers. While all bus interchanges have passenger facilities, not all bus terminals allow for passenger boarding and alighting. Bus interchanges/terminals also double as overnight parking spaces for public buses, due to the lack of parking space within bus depots. This practice was common in the early 2010s but has since been reduced, with the construction of more bus depots and bus parks. Facilities: Bus interchanges (and some terminals) have one or more of such facilities:
Bus Services: 110, 374
Bus Services: 7, 9, 14, 16, 17/17A, 18, 25, 26, 30, 30e, 32, 33, 35, 38, 40, 60, 66, 69, 87, 168, 196, 197, 222, 225G, 225W, 228, 229, 401, 854, 854E
Bus Services: 75, 184
Bus Services: 160, 170X, 950, AC7, TS1, TS8
Bus Service: 975
Bus Service: 402
Bus Services: 2, 12, 12e, 54, 120, 121, 122, 174, 174e, 190, CT8, CT18
Bus Service: 63
Bus Services: 70, 106, 107, 128, 130, 133, 162, 186, 400, 402, 700, 970
Bus Service: 49
Bus Services: 192, 193, 247, 248
Bus Services: 161, 168, 169, 178, 187, 856, 858, 900, 900A, 901, 902, 903, 903P, 904, 911, 912, 912P, 913, 925, 925#, 926, 950, 960, 961, 961#, 962, 963, 963E, 963R, 964, 965, 966, 969
Bus Services: 39, 85, 171, 800, 803, 804, 806, 811, 811P, 812, 812P, 851, 852, 853, 853#, 854, 854E, 855, 856, 857, 859, 860, AC7
Bus Services: 39, 85, 103, 171, 800, 803, 804, 805, 806, 807, 811, 812, 851, 851e, 852, 853, 853#, 854, 854e, 855, 856, 857, 859, 860, AC7
Service 146
Service 115
Service 53M
Services 42 & 135
Service 230 (Planned amendment in Feb 2025)
Detailed History:
Current operations:
Staffed by the bus operators, this office is the management center of any bus interchange. It handles passenger inquiries, timekeeping for bus services and various other interchange operations. They usually have a computer terminal for drivers to clock the start and end of their scheduled trips.
Staffed by TransitLink personnel, this office mainly handles contactless card transactions among other services.
Where bus drivers take a break before their next departure.
The National Transport Workers’ Union (NTWU) manages a group of canteens known as NTWU canteens which are commonly found at major bus interchanges. They provide healthy and low-cost meals for bus drivers, and are also open to members of the public.
Berths are pick-up areas for buses. Most major interchanges have three services assigned to a berth, with queuing areas for passengers.
Buses terminating at the interchange drop off passengers here before heading to park
Public transport operators design various information boards for their interchanges such as locality maps, bus service maps and bus information.
This electronic bus arrival board contains timings of the next scheduled bus departure.
The service guide rack is stocked with paper guides containing details of various bus services.
In recent years, bus operators have opened various stalls at their bus interchanges to increase profits by renting them out to vendors. Food stalls are among the most common.
Some bus interchanges charge a small fee for members of the public.












If bus 27 is from Hougang Central Bus Interchange to Changi Airport
You have to cross over TPE Expressway berth 1a/1b and then loop back.
If Hougang South Int is Defunct,It can be replaced by the Hougang Central Bus Interchange.
Current Predictions of Upcoming Bus Interchanges to be part of ITH:
Under Planning/Work In Progress:
Woodleigh, Pasir Ris, Punggol Coast, Jurong East, Tengah, Beauty World, Kallang, Bedok South, Hougang, Tampines, Tampines North, Choa Chu Kang, Woodlands North, Marina South, Punggol (Highly Possible)
TBD:
Harbourfront, Eunos, Bukit Batok, Yio Chu Kang, Bishan, Sembawang, Chencharu, Tiong Bahru
Interchanges in need of a sub-interchange (e.g compassvale, tampines concourse)
– Tanah Merah Interchange (Extension to Bedok Int); Consist of services 7, 16, 32, 33, 60, 87 & 155
– Lakeside Interchange (Extenstion to Boon Lay Int); Consist of services 154, 157, 174 & 198
– Yew Tee Interchange (Extension to Choa Chu Kang Int); Consist of services 172, 188, 925 & 983
– Ulu Pandan Terminal (Extension to Clementi Int); Consist of services 7, 14, 96, 165 & 173